Behaviour structure¶
Evacu-agent pedestrians all have the ability to contain multiple sets of behaviours. Each set of behaviours will be exhibited in a given environment or scenario, such as in crowded stadiums or in evacuation events.
Behaviours and sets of behaviours are structured in a hierarchy, with the currently active set of behaviours modelled as a reactive subsumption hierarchy. This hierarchy represents the preference in which behaviours will be triggered, with the highest priority behaviour being considered first and the lowest priority behaviour being considered last.
The behaviour hierarchy is a child of the Pedestrian GameObject as described in the diagram below:
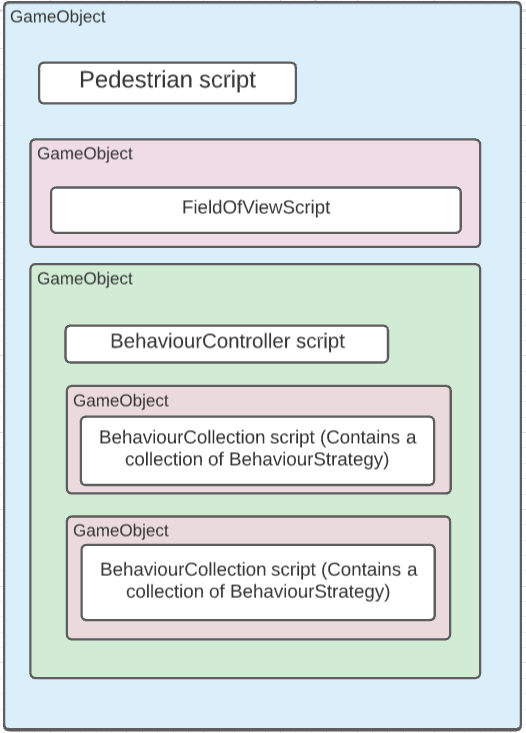
The structure¶
Behaviour Controller¶
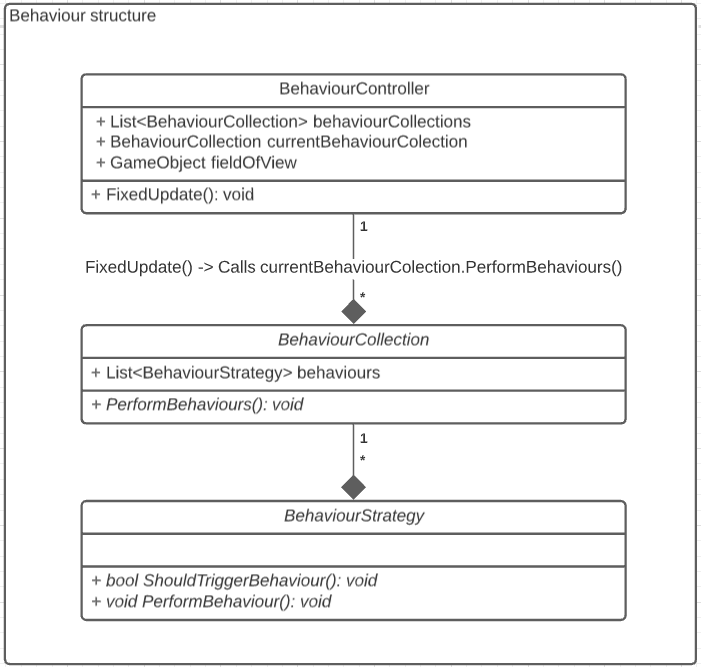
BehaviourController - Each pedestrian has exactly one of these controllers.
It is responsible for maintaining a List<BehaviourCollection> which stores all behaviours a pedestrian is able to perform.
It also tracks the active BehaviourCollection, so that the collection of behaviours appropriate for the current context can be dereferenced.
FixedUpdate() is used to call currentBehaviourCollection.PerformBehaviours().
Behaviour Collection¶
BehaviourCollection - Models a set of related behaviours that a pedestrian is able to use in a given context. It does this via storing a List<BehaviourStrategy>.
The sole method PerformBehaviours() then iterates over this collection of BehaviourStrategy, calling behaviourStrategy.ShouldTriggerBehaviour() which checks to see if the conditions of each given behaviour to trigger are currently met.
If conditions are correct for a given behaviour to execute then behaviourStrategy.PerformBehaviour() is called on that BehaviourStrategy.
Note the iteration stops once a behaviour has been triggered, to ensure only one behaviour is executed per iteration.
Behaviour Strategy¶
BehaviourStrategy - Is responsible for modelling a single behaviour, such as entering a building or choosing a path of nodes to visit.
This is an abstract class containing two abstract methods:
-
public abstract bool ShouldTriggerBehaviour()- In each behaviour this method contains logic to check whether the behaviour should be executed. This is done through using percept information such as that obtained from the FieldOfView. -
public abstract void PerformBehaviour()- In each behaviour this method contains the logic for execution of that given behaviour, for example choosing a path of nodes to visit.
Below is an example of a BehaviourStrategy called WaitAtDestinationBehaviour.
It checks to see if a pedestrian is at its destination in ShouldTriggerBehaviour() and stops the pedestrian moving in PerformBehaviour().
public override bool ShouldTriggerBehaviour()
{
float distanceToDestination = Vector3.Distance(transform.position, groupCollection.GroupDestination);
return distanceToDestination <= RadiusToDestination;
}
public override void PerformBehaviour()
{
evacuAgentPedestrianBase.ChangeSpeedToMatchLeader(normalSpeed);
evacuAgentPedestrianBase.IsPedestrianMovementStopped(false);
}
Behaviour Type Order and Behaviour Type¶
Behaviour Type Order¶
BehaviourTypeOrder - This is responsible for storing the List<BehaviourStrategy> for a given BehaviourCollection for different types of pedestrians.
The order that behaviours is stored here is important as elements closer to index 0 will be considered for execution first, and only one behaviour is triggered per iteration.
BehaviourTypeOrder is an abstract class declaring one protected property and one abstract method:
-
protected List<BehaviourType> behaviourTypes- Models theList<BehaviourStrategy>used for defining the preference order of behaviour execution. This is set up inAwake()of eachBehaviourTypeOrder. -
public abstract List<BehaviourType> GetBehaviourTypes()- ReturnsbehaviourTypes.
Behaviour Type¶
BehaviourType - This is responsible for storing a reference to a BehaviourStrategy script that will be instantiated and added to a BehaviourCollection for a pedestrian to use.
This is an abstract class declaring two methods:
-
public abstract Type GetBehaviourStrategyClass<T>() where T : BehaviourStrategy;- Returns a type ofBehaviourStrategyto be instantiated. -
public abstract float GetBehaviourStrategyChance()- Returns a float between 0 and 1 that represents the chance of aBehaviourStrategybeing added to aBehaviourCollection. Currently this is not used but it is intended to allow pedestrians drawing behaviours from the sameBehaviourTypeOrderto have non-uniform behaviour.
Example¶
In the example below, FriendGroupLeaderTypeOrder defines the preference order of behaviours to be used by a FriendGroupLeaderPedestrian.
The private classes are used to populate behaviour types which store references to two BehaviourStrategy:
GenericEnterLeaveBuildingBehaviour.GenericPathCreationBehaviour.
The List<BehaviourType> behaviourTypes object is instantiated and populated in Awake().
When behaviourTypes is passed to a pedestrian it will allow the BehaviourStrategy to be instantiated and added in the correct order, where GenericEnterLeaveBuildingBehaviour will be added first, GenericPathCreationBehaviour second and the rest of the BehaviourType in the correct order.
This means that whilst the BehaviourCollection containing these behaviours is actively being iterated over, the behaviours will be iterated over in the order they are added, giving highest priority to GenericEnterLeaveBuildingBehaviour.
public class FriendGroupLeaderTypeOrder : BehaviourTypeOrder
{
private void Awake()
{
behaviourTypes = new List<BehaviourType>()
{
new GenericPathCreationBehaviourType(),
new GenericEnterLeaveBuildingBehaviourType(),
new WaitForFollowersBehaviourType(),
new WaitAtDestinationBehaviourType(),
new FriendGroupBoidBehaviourType(),
new GenericNoNewBehaviourType()
};
}
public override List<BehaviourType> GetBehaviourTypes() => behaviourTypes;
private class GenericEnterLeaveBuildingBehaviourType : BehaviourType
{
private readonly float behaviourStrategyChanceToUse = 1f;
public override Type GetBehaviourStrategyClass<BehaviourStrategy>() => typeof(GenericEnterLeaveBuildingBehaviour);
public override float GetBehaviourStrategyChance() => behaviourStrategyChanceToUse;
}
private class GenericPathCreationBehaviourType : BehaviourType
{
private readonly float behaviourStrategyChanceToUse = 1f;
public override Type GetBehaviourStrategyClass<BehaviourStrategy>() => typeof(GenericPathCreationBehaviour);
public override float GetBehaviourStrategyChance() => behaviourStrategyChanceToUse;
}
// Further details omitted
}
Adding a new behaviour to an existing Behaviour Collection¶
-
Create a new script that extends
BehaviourStrategyin an appropriate folder inAssets/Scripts/EvacuAgentwith a folder suffixed with Behaviours or add a new folder also suffixed with Beahviours. The new script should be suffixed with Behaviour. -
Add a private class extending
BehaviourTypein the appropriateBehaviourTypeOrder. Inside the class, the methodGetBehaviourStrategyChance()should return a float between0and1. The return type ofGetBehaviourStrategyClass()should look similar totypeof(NewBehaviourScriptType). -
The new private class should be instantiated in
behaviourTypesin theAwake()method of theBehaviourTypeOrder.
Adding a new Behaviour Collection¶
-
Create a new script extending
BehaviourTypeOrderinAssets/Scripts/EvacuAgent/BehaviourTypessuffixed with Behaviours. The script name should be suffixed withTypeOrder. -
Add an
Awake()method which instantiatesbehaviourTypes. -
Ensure that
GetBehaviourTypes()returnsbehaviourTypes. -
Add the necessary number of private classes that extend
BehaviourTypeas described in Adding a new behaviour to an existing Behaviour Collection: Step 2. -
Populate the
behaviourTypesinstance with theBehaviourTypecreated in the previous step. Remember that order of these is important, behaviours will be iterated from element0to elementN. -
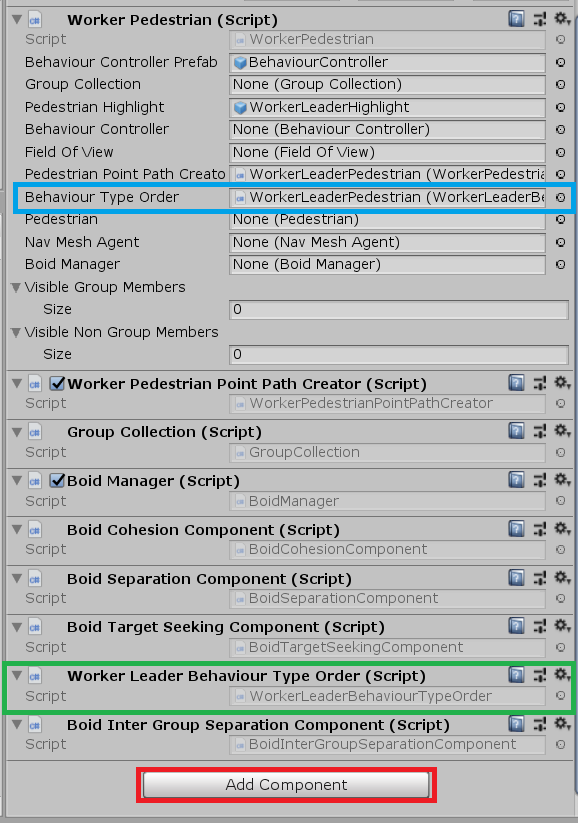
Add the new
BehaviourTypeOrderscript to the appropriate pedestrian prefab using Add Component as seen in the diagram below in red. This should make theBehaviourTypeOrderappear on theGameObject, as seen in green. Finally drag and drop theBehaviourTypeOrderinto the slot marked in blue.